Criminal licensing
For many years, software producers have been refining their revenue-generating schemes. While at the dawn of the computer era, all software could be divided into two major categories—commercial software and freeware, with the passing of time, the situation changed dramatically.
Back in the late nineties, the American company Netscape Communications Corporation released the browser Netscape Communicator, offering users a completely different licensing scheme called shareware. The browser was distributed free of charge from Netscape's site, but after a short trial period, the company asked users to voluntarily pay for the application. This approach was soon adopted by other software developers.
Another business model called freemium became popular when massive online multiplayer games appeared. Under this model, games are provided free of charge. However, to achieve better results or purchase more powerful units or items, players have to pay a certain sum of money.
Finally, the SaaS business model—Software as a Service—appeared on the market somewhat recently. Under the SaaS model, access to an application is provided for a set amount of time on a fee basis. It was this model that cybercriminals adopted.
CaaS (Crime as a Service), which is a model along the same lines as SaaS, is used by criminals to distribute malware. Resourceful criminals wanting to earn extra money off the distribution of malware offer the opportunity to buy a license to rent a Trojan horse, complete with control panel and usage guide, so that anyone who wants to spread viruses can install it on their own server. By spreading a Trojan, a criminal can establish a botnet that will generate illicit profits.
This illegal licensing model was used by the criminals behind the mobile banking Trojan Android.SmsSpy.88.origin.
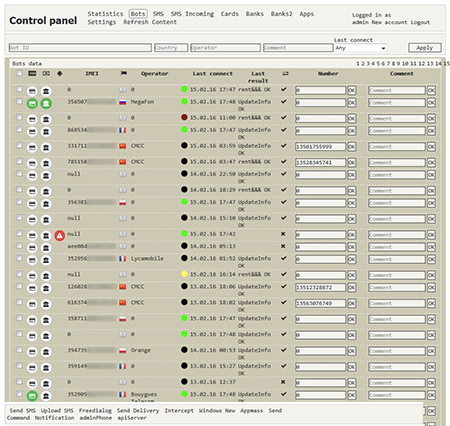
They advertise the malware on various underground forums, selling the Trojan as a commercial product. Criminals who buy this malware receive the server component bundled with an administration panel that facilitates control over devices infected by the malware. A panel of this kind may look like this:
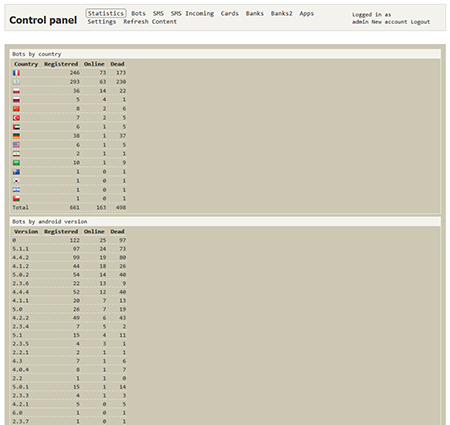
Control panels offer criminals detailed infection statistics, display information about stolen logins and passwords, and enable them to control their botnets. By spreading Trojan horses in a variety of ways, cybercriminals make up for their license purchase costs and generate unlawful revenue.
Many Trojans for various platforms, including Windows and Android, are distributed under this model.
This, in part, accounts for the constant growth in the number of malicious samples that enter Doctor Web's anti-virus laboratory on a daily basis. Today, the fight against the people behind criminal licensing schemes is a priority for anti-virus companies and law enforcement agencies throughout the world.


![Shared 15 times [Twitter]](http://st.drweb.com/static/new-www/social/no_radius/twitter.png)
Tell us what you think
To leave a comment, you need to log in under your Doctor Web site account. If you don't have an account yet, you can create one.
Comments
vasvet
06:27:26 2018-07-26